Offering Description
- Direct technology search
- Limited analysis using smaller team
- Substantiation is not includedSuggested for initial project as trust-building step or for customers with limited budget
Background
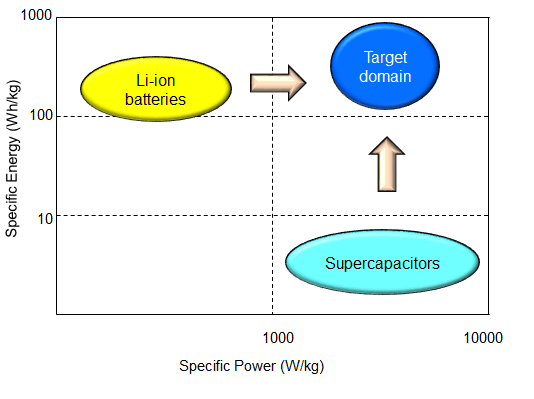
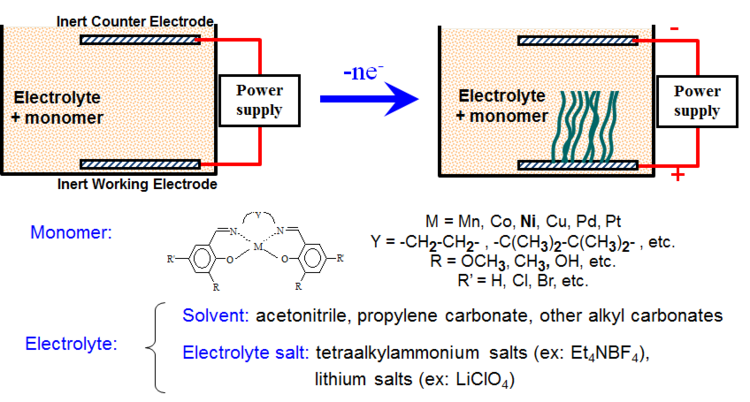
Energy Storage Device:
- Li-ion batteries have pretty high capacity, but they cannot discharge large energy (and also they need a lot of time to be charged)
- On the contrary, supercapacitors can discharge a lot of energy and have relatively short charging time, but they have insufficient capacity
- Therefore, it is necessary to find perspective technology capable to provide both high capacity and high discharge energy
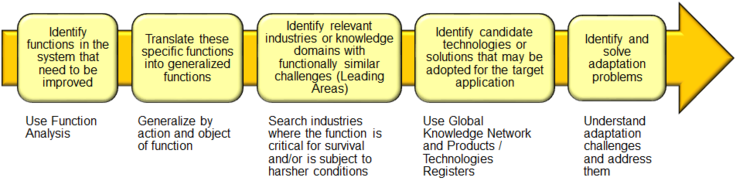
Main Tool of Technology Scouting: Function-Oriented Search
Function-Oriented Search is a TRIZ tool that helps to identify existing technologies in leading areas of science and engineering, using functional criteria.
Application of Function-Oriented Search
- A Li-ion battery stores a lot of energy due to reversible chemical reaction
- A supercapacitor can discharge a lot of energy due to absence of a mass transfer
- Thus it is necessary to find a technology that can effectively and reversibly convert chemical energy to electrical energy without a mass transfer
-
Leading Area:
- Chemically active polymers
-
Found Technology:
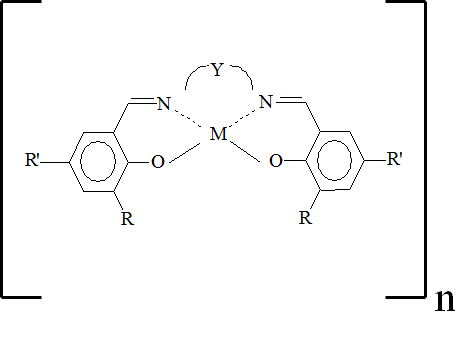
- Poly[M(Schiff)] redox polymers
- This polymers can reversibly change redox potential => they can store electric energy in chemical form, but reversible chemical reaction does not need a mass transfer
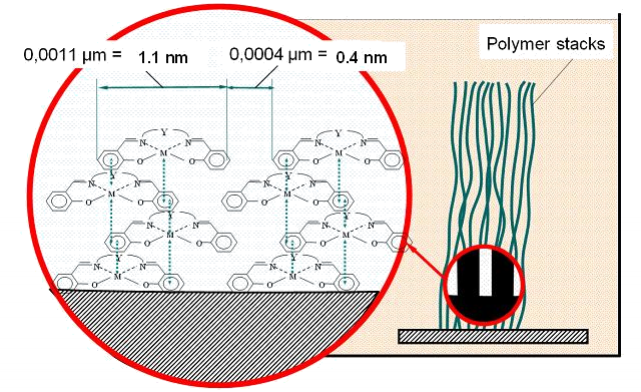
Description of Found Technology: AESD
- Broad potential range of electrochemical activity (> 3 V)
- High specific energy stored in the polymer (> 300 J/g)
- Unique thermal stability (up to 350°C)
- High chemical and electrochemical reversibility of redox processes
- Easy synthesis and low cost
- Work in the same electrolytes and at the same potentials as Ultracapacitors and Lithium-ion batteries.
Due to their unique properties, polymer Schiff base transition metal complexes (Poly[M(Schiff)]) are promising materials for energy storage applications.
Polymer properties can be easily tuned by proper selection of monomer and electrolyte composition and polymerization conditions (voltage, duration, etc.)
Results and Conclusions
-
Results:
- Using GEN TRIZ methodology of TRIZ-based Technology Scouting there was found the technology of energy storage having high potential for various applications
- Number of investors found this technology promising enough to organize the startup EnGen that works on commercialization of this technology
-
Conclusions
- GEN TRIZ methodology of Technology Scouting is highly effective and practically tested
- Using this methodology GEN TRIZ can help Clients to identify and select necessary technologies that meet all pre-defined requirements and restrictions
Offering Description
- Product/Process Improvement
- In-depth analysis of a product or process related problem to find underlying key problems
- Solution development suitable for different time lines (incremental as well as disruptive ideas)
- Much more comprehensive than Tech Scouting
Background
- A car body includes number of aluminum sheet parts with complex shape.
- The current technology includes sheet extrusion, multi-step stamping and welding.
- Due to large number of operations and applying complex equipment, the current technology is too expensive
- It is necessary to reduce operation cost dramatically
- What should be done?
- Solutions substantiation (reasons to believe)
- Support for IP (patent) preparation
Trimming and Physical Contradiction
-
The problem:
- How to reduce the operation cost?
-
Trimming:
- It is necessary to exclude majority of operations from the technological process and delegate their useful functions to one operation: extrusion
-
Trimming problem:
- How to extrude an aluminum sheet with complex shape?
-
Physical contradiction:
- The die should have one particular shape to provide specific cross-section of the aluminum sheet, but it should have another shape to provide another cross-section
- Separation in time: the die should be able to change its shape in the process of aluminum sheet extrusion
- Inventive Principle: Dynamicity (divide an object to parts capable to move relatively each other.
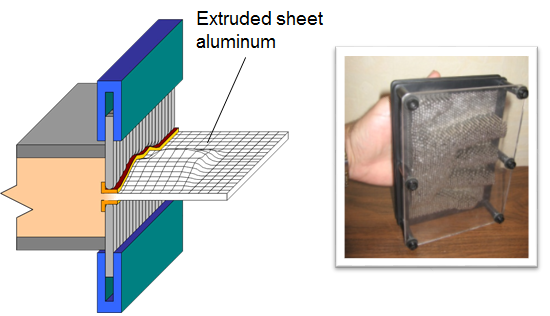
Solution: Dynamic Extrusion
Idea Description:
- Extrude aluminum sheet with complex shape using existing dies and additional equipment
Benefits:
- Reduced number of steps in the technological process
- Reduced tooling costs
- Productivity close to that of conventional extrusion
- Higher quality of the produced components, which are shaped when aluminum is in a malleable solid state; stamping aluminum in a solid state leads to high stress areas
- Option to change the shape (design flexibility) in terms of thickness and profile
- Weight savings due to improved mechanical performance
Offering Description
- Identification of market needs and MPVs
- Technology and IP Landscaping
- New product/process portrait development
- Enabling technologies identification
- IP evaluation and protection
Background
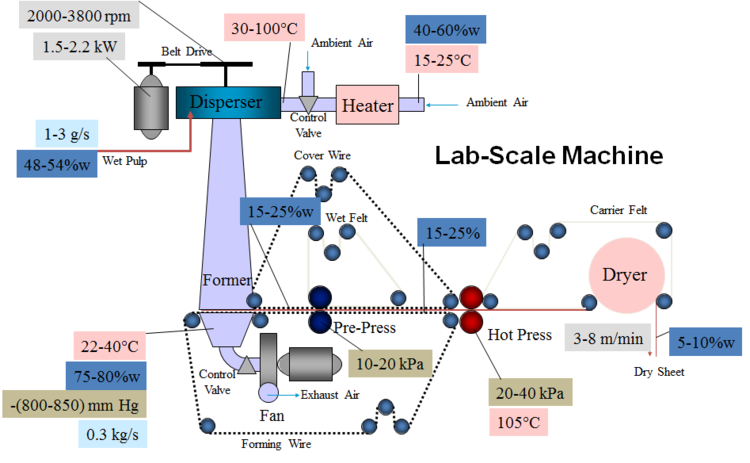
- Although the paper industry has substantially improved its technology in the face of increasingly stringent environmental requirements, 99% of paper is still made using a water-laid process
- When paper is volume-produced using water-laid technology, the process is extremely water- and energy-intensive; the water-paper slurry is more than 99% water (500-1,000 kg of water/kg of dry paper), and the dryers consume large amounts of energy. Reducing water and energy consumption of the papermaking process would decrease capital and operating costs substantially.
- Project goal: It is necessary to forecast a new generation of paper production technology that can produce paper of the same quality with a minimal amount of water
Radical Trimming
Problem Solving
-
The Problem:
- How to distribute fibers without water?
-
Physical contradiction:
- It is necessary to use large amount of water to distribute cellulose fibers effectively, but it is necessary to have no water to eliminate paper drying and thus significantly reduce energy consumption
-
Method of resolving:
- Satisfying contradictory requirements
-
Inventive Principle:
- Changing of physical stage (phase transition)
-
Idea of solution:
- Distribute cellulose fibers with steam => large amount of water is not necessary
- Small amount of condensing water will bind cellulose fibers
Solution: Low Moist Paper Making Process
Offering Description
- Finding adjacent applications for existing Client’s products, technologies, materials and patents to monetize / commercialize customer’s existing intellectual assets
- Audit client’s product, component, technology, patents and their features and functions. Find out where these functions are applicable and important in other markets
- Business information such as market size and potential partners may also be delivered
Reverse Function-Oriented Search – Major Tool for Adjacent Market Identification
- The goal of Reversed Function-Oriented Search (RFOS) is to identify industries where existing technologies and products can be applied.
- Industries face similar engineering challenges, but the similarities are not always obvious because these industries are often completely different in their focus.
- RFOS removes the industry-specific limitations of potential areas of an existing technology application and uncovers possibilities, regardless of the source industry.
- RFOS breaks psychological barriersfor acceptance of new areas of application because there is already proof that the initial technology will work in similar conditions.
- RFOS allows utilization of all functions, including harmful and additional ones.
- RFOS allows utilization of not only functions, but also properties which can become resources for potential functions.
Algorithm of Reverse Function-Oriented Search
- Perform an audit (examination) of client’s portfolio of products and technologies that constitute client’s core competencies and competitive advantages.
- Select an object for RFOS (product or technology)
- Build a component model of the selected object
- Select one of the components or the entire product/technology
- Formulate all its properties (physical, chemical, geometrical, etc.)
- Select one of the properties
- Convert the selected property to a set of functions
- Select one of the functions
- Generalize the selected function
- Identify a leading area, in which similar functions and properties are very important and that has the biggest business potential
- Identify in the selected area a specific function similar to the generalized function
- Using the identified function as a new main function of the initial object, formulate an adaptation problem: “How to make the object perform the new main function”
- Solve the adaptation problem
- If necessary, repeat the algorithm for another function, property, and component
- Develop value proposition for each identified adjacent area of application
- Search for potential partners and/or buyers in the selected area.
Example: Cable Insulation Monitoring
- Select an object for RFOS
Technology of identification of the internal composition of a cable insulator, based on non-invasive measurement of its electrical impedance - Selected function (main function)
To measure the amount of water in a cable insulator (i.e., to inform a person about the presence and amount of water) - Formulate its advantages (the function can be performed under unique conditions, can provide unusual results, etc.)
Non-invasive measurement; results can be achieved immediately; compact, inexpensive, and fully automated equipment - Generalize the function
To measure amount of a selected substance in a complex multi-phase structure - Identify a leading area, in which similar functions and their advantages are very important
Monitoring of a blood composition for medical purposes - Identify a real object in the selected area similar to the generalized object of the generalized main function
Glucose - Redirect action of the main function to the identified object
To non-invasively measure the amount of glucose in a patients’ blood - Using reformulated function as a new main function of the analyzed object, formulate an adaptation problem: “How can the object be made to perform this new main function?”
How to adapt existing technology of a cable insulator control device for constant real- time non-invasive monitoring of blood glucose for patients with diabetes? - Solve the adaptation problem. Business case
Healbe company started commercializing a new device in 2015 https://healbe.com/us/
Offering Description
- Setting up a team of subject matter experts, TRIZ specialists and GKN experts
- Identification of target MPVs
- Conceptual design of new product/process
- Enabling technologies identification
- Proof-of-principle prototyping
Background
- There are number of hands sanitizers that could be used occasionally somewhere out of sanitizing facilities
- All of them have number of disadvantages:
- Excessive cost
- Excessive skin drying
- Existing lotions compensating the skin drying provide a friendly environment for harmful bacteria and dirt. Also they eliminate subjective feeling of the skin cleanliness and have excessive cost
- Lack of a “wow effect” necessary to attract more customers
- Project goals:
- Main Goal:
- Develop a new product with high “wow effect”
- Additional Goals:
- Reduce cost
- Provide subjective feeling of cleanliness
- Main Goal:
Radical Trimming
Application of Standard Inventive Solutions
Application of Function-Oriented Search
The same function as surfactant is performed in washing machine by electrically activated water
Detergentless Haier WasH20 Washing Mashine
Haier WasH20 just came with a new and innovative washing machine, that can save you the money you spend on detergent or soap. The Haier WasH2O washing machine doesn’t use any detergents!!! This washing machine works by breaking water molecules into its OH- and H+ ions components. OH- acts as the cleaning agent by attracting and retaining stains while the H+ ions sterilizes the clothes.
http://freshome.com/2007/07/31/detergentless-haier-wash20-washing-machine/
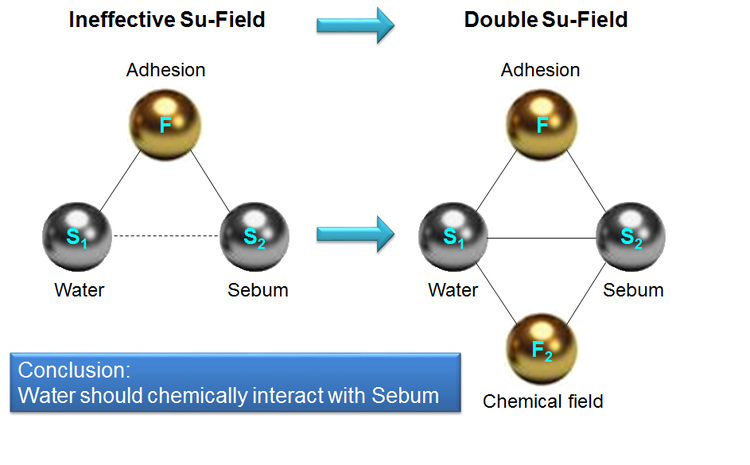
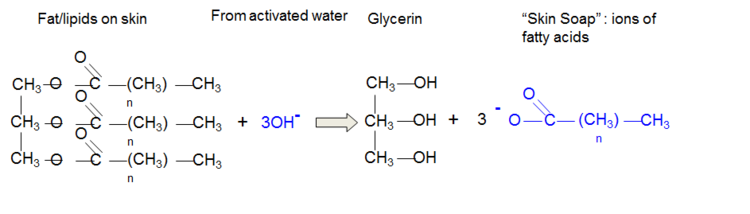
Activated Water: “Teach Sebum to do the Job of Surfactant”
The principle: electrically activated alkaline water (catholyte) makes sebum a surfactant
Advantages
- Sebum produces surfactant => no excessive amount of surfactant => no skin irritation + no excessive removing of skin moisture => no lotion is necessary => good feeling of cleanliness + low cost
- Sebum produces surfactant => no external surfactant => low cost
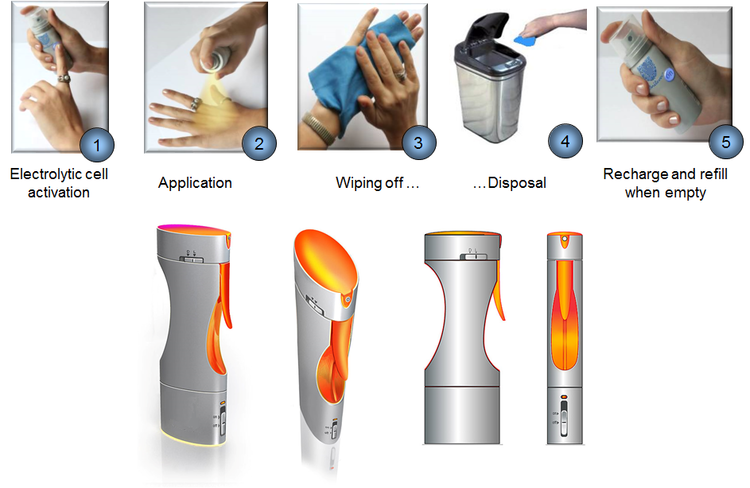
- No external surfactant + no lotion => the bottle can be refilled with water from any available source => high convenience + low cost
- No external surfactant => no excessive amount of water is necessary to remove it => small bottle => high convenience + low cost
- High “wow effect”
Offering Description
- 1-2 consultants and professional patent attorney
- Determine how to not violate a competitive patent and prevent infringement
Background
- Scenario:
- The Independent claim of a patent describes a toothbrush thatconsists of a head containing bristles, and a handle that holds the head.
- The handle and head also hold an electrode that is powered by a battery inside the handle
- The electrode ionizes air for easy plaque removal
- Project Goal:
- It is necessary to circumvent this patent
Trimming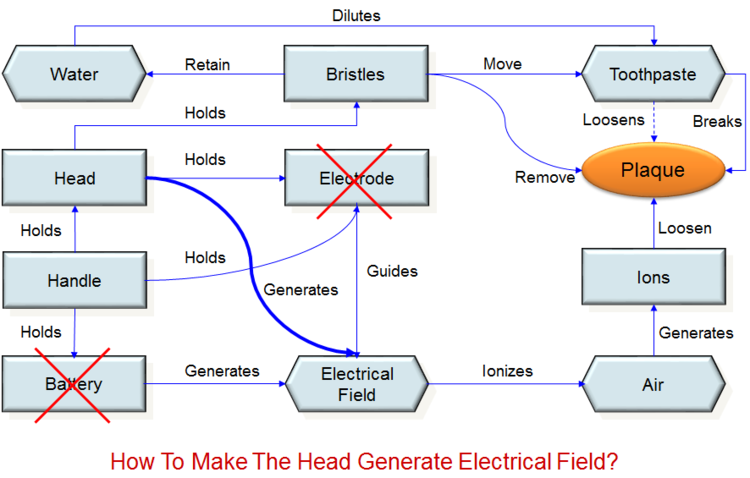
Solution
- The toothbrush head surface is covered with an alloy that, when in contact with toothpaste and water, works as an active couple and generates voltage.
- As a result the head itself ionizes the air near the plaque
Offering Description
- Voice of the Product Analysis (VOP)
- Latent MPVs identification
- Voice of the Customer (VOC) evaluation using newly discovered MPV candidates
Background
- Initial Situation:
- The market of toothbrushes is overcrowded and thus competition is very intensive. Regular methods of the product improvement are almost exhausted.
- Object:
- Regular toothbrush
- Business Challenge:
- How to make a toothbrush that would be the market winner?
MPV Analysis
- Known MPVs:
- Cleaning effectiveness
- Convenience
- Operational time
- Unknown MPV:
- Toothbrush aseptic (warm, wet, dark environment and large surface area of bristles make a toothbrush the perfect incubator for bacteria)
Solutions
- Keep a toothbrush in a refrigerator
- Keep a toothbrush in a mouthwash
Offering Description
- Set up R&D labs for customers
- Conceptual design, prototyping, testing, secondary problem identification and solving
- Combines TRIZ expert + subject matter experts
- Lower operating costs that possible in Client’s country
- Fast and reliable results
- Customers welcome to visit periodically
Background
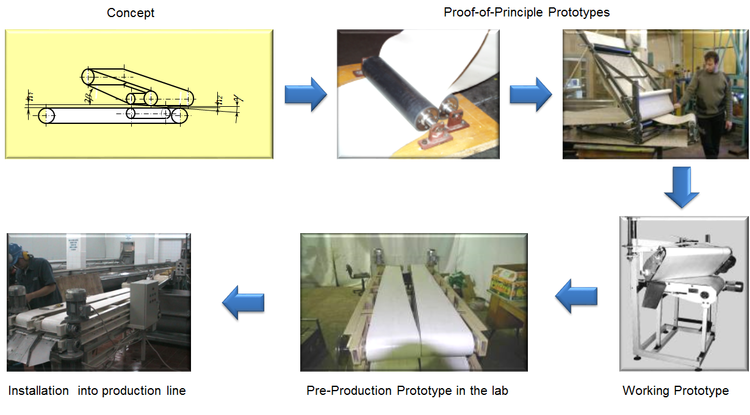
It was necessary to develop effective method of banana peeling.
Requirements:
- No damaging of a banana
- High productivity
- High reliability
- Low cost
We developed integral concept, that included two non-parallel conveyors that orient bananas, and peeling mechanism that gently removed banana peel with no damaging of a fruit body
After that we developed:
- Number of proof-of-principle prototypes
- Working prototype
- Pre-production lab-scale prototype
- Full-scale working equipment
Offering Description
- Failure Explanation technique identifies the cause of a defect in the product or bottleneck in the process
- Failure Anticipation technique produces hypotheses of most probable product or technology failure
Background
- Scenario:
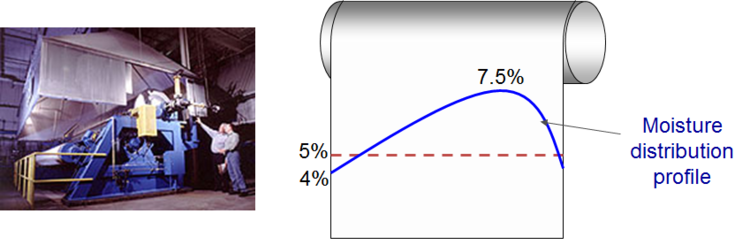
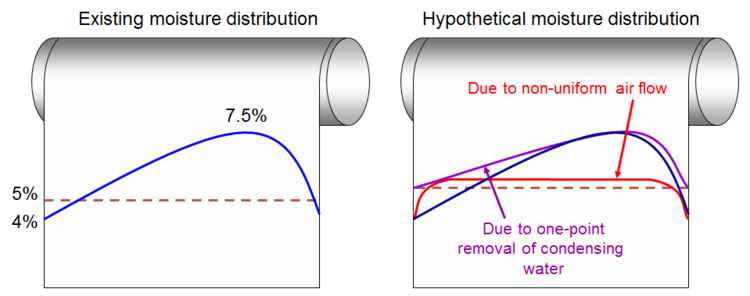
- A company produces paper which is used to manufacture cardboard. The production process has the following disadvantage: non-uniform moisture distribution within the paper. This non-uniformity eventually leads to curling of the cardboard. Despite many attempts, the company has been unable to identify the cause of this problem.
- Challenges:
- Uncover the hidden causes of the non-uniformity of moisture in paper
- Develop disadvantage-prevention concepts
Hypotheses
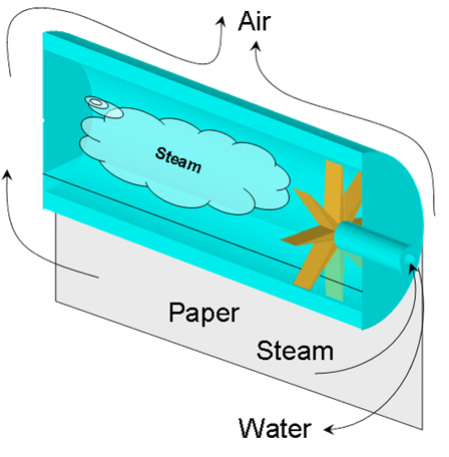
- One-point removal of condensing water can provide non-uniform drum cooling
- Non-uniform air flow around the drum can create non-uniform distribution of moisture in the paper
Practical Validity of Proposed Solution
Expert opinion:
- Both described phenomena exist
- Both phenomena together can provide existing non-uniform moisture distribution
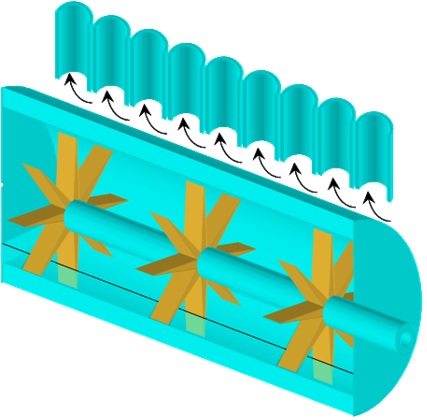
Recommendations
Install multi-point air- and water removal systems